Super Heavy Duty Gas Spring with Reinforced Structure
Patent No.:CN101566208 Date:2009-06-15
Google Patent: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN101566208A/en?oq=CN101566208
China Patent: http://epub.cnipa.gov.cn/
Abstract
This invention relates to a gas spring, specifically to a high-force gas spring with a reinforced structure. The technical problem this invention aims to solve is to provide a Super Heavy Duty gas spring with a reinforced structure that enhances its service life. It includes a cylinder, a piston, and its piston rod. The end of the cylinder is welded with a rear seal, and a piston is installed inside the cylinder. The front end is welded with a guide sleeve through which the piston rod passes and connects to the piston. The joints between the guide sleeve, the rear seal, and the cylinder’s inner wall are connected first by threaded sliding fit and then welded or folded. A guide ring is installed on the outer circumferential surface of the piston. The guide sleeve and the rear seal are connected to the cylinder through threaded sliding fit and welding or folding, which enhances their connection strength and ensures safety under high pressure. A guide ring is added to the piston ring to ensure the concentricity of the gas spring cylinder with the piston and piston rod, reducing wear and increasing the service life of the gas spring.
Description
Super Heavy Duty Gas Spring with Reinforced Structure
Technical Field This invention relates to a gas spring, specifically to a Super Heavy Duty gas spring with a reinforced structure.
Background Technology With the widespread application of gas springs in medical equipment, automobiles, furniture, textile equipment, and the processing industry, there is an increasing demand for higher force values. Traditional guide sleeves are fixed by folding the edges of the cylinder or by welding, bearing the pressure from the internal pressure of the cylinder. Ordinary edge folding or welding cannot withstand the high forces, leading to safety issues in manufacturing heavy duty gas springs. There is also a certain gap between the piston and the cylinder wall in ordinary gas springs, causing the piston to scrape the inner wall and seals during movement, leading to wear on the guide sleeve or piston rod and reducing the gas spring’s service life.
Summary of the Invention The technical problem this invention aims to solve is to provide a high-force gas spring with a reinforced structure that enhances its service life.
To solve the above technical problems, the invention’s technical solution is: a super heavy duty gas spring with a reinforced structure, comprising a cylinder, a piston, and its piston rod. The end of the cylinder is welded with a rear seal, and a piston is installed inside the cylinder. The front end is welded with a guide sleeve, and the piston rod passes through the guide sleeve to connect to the piston. The innovation is that the joints between the guide sleeve, the rear seal, and the cylinder’s inner wall are connected first by threaded sliding fit and then welded or folded; the piston is equipped with a guide ring.
Advantages of the Invention The guide sleeve and the rear seal are connected first by threaded sliding fit and then welded or folded, enhancing the connection strength and ensuring safety under high pressure. Adding a guide ring to the piston ensures the concentricity of the gas spring cylinder with the piston and piston rod, reducing wear and increasing the service life of the gas spring. A unidirectional valve-type inflation port on the rear seal makes inflation more convenient and safe.
Description of Drawings
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the gas spring structure of the invention.
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of the piston structure of the gas spring of the invention.
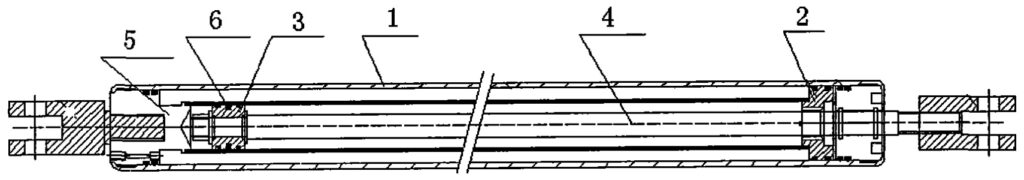
Detailed Implementation As shown in Figures 1 and 2, it includes a cylinder 1, rear seal 5, piston 3, guide sleeve 2, piston rod 4, and guide ring 6.
The end of the cylinder 1 is welded with a rear seal 5, and a piston 3 is installed inside the cylinder. The front end is welded with a guide sleeve 2, and the piston rod 4 passes through the guide sleeve 2 to connect to the piston 3.
Since the guide sleeve 2 and the rear seal 5 are welded to the cylinder 1, both bear half the pressure generated by the internal pressure of the cylinder 1. This type of sealed gas spring is difficult to withstand internal pressure, posing safety risks, making it challenging to manufacture heavy duty gas springs. Now, the outer walls of the guide sleeve 2 and the rear seal 5 are provided with external threads, and the inner wall of the cylinder 1 is provided with internal threads. The guide sleeve 2 and the rear seal 5 are connected to the cylinder 1 by internal and external threaded sliding fit and are welded to strengthen the connection, ensuring the safety of the gas spring.
Theoretically, there is a certain gap between the piston 3 and the inner wall of the cylinder 1, causing the piston 3 to scrape the inner wall of the cylinder 1 and the guide sleeve 2 during movement, leading to wear on the guide sleeve 2 or the piston rod 4. This problem is often overlooked in common gas spring design, as concentricity between the piston 3, piston rod 4, and the inner circle of the cylinder 1 is often ignored. As shown in Figure 2, a wear-resistant guide ring 6 is installed on the outer circumferential surface of the piston 3. The guide ring 6 supports the piston 3 and the piston rod 4 in the middle of the inner wall of the cylinder 1, ensuring the concentricity of the inner wall of the cylinder 1 with the piston 3 and the piston rod 4 during the movement of the gas spring, reducing wear on the guide sleeve 2 and the piston rod 4, and improving its service life.
Claims (4) – Super Heavy Duty Gas Spring with Reinforced Structure patent by LeiYan
- A super heavy duty Gas Spring with Reinforced Structure, comprising a cylinder, piston, and its piston rod. The end of the cylinder is welded with a rear seal, and a piston is installed inside the cylinder. The front end is welded with a guide sleeve through which the piston rod passes to connect to the piston. It is characterized by: the joints between the guide sleeve, rear seal, and the inner wall of the cylinder are connected first by threaded sliding fit and then welded or folded; the piston is equipped with a guide ring.
